What Is Runner’s Knee and How Do I Fix It?
As a runner, you may have heard of “runner’s knee” or experienced it yourself. It’s a common condition that affects many runners, and it can be both painful and frustrating. But what exactly is runner’s knee, and how can you fix it?
Let’s talk about the causes of runner’s knee, as well as some strategies for preventing and treating the condition. Whether you’re a casual jogger or a seasoned marathoner, understanding runner’s knee is essential for keeping your running routine pain-free and enjoyable.
Understanding Runner’s Knee
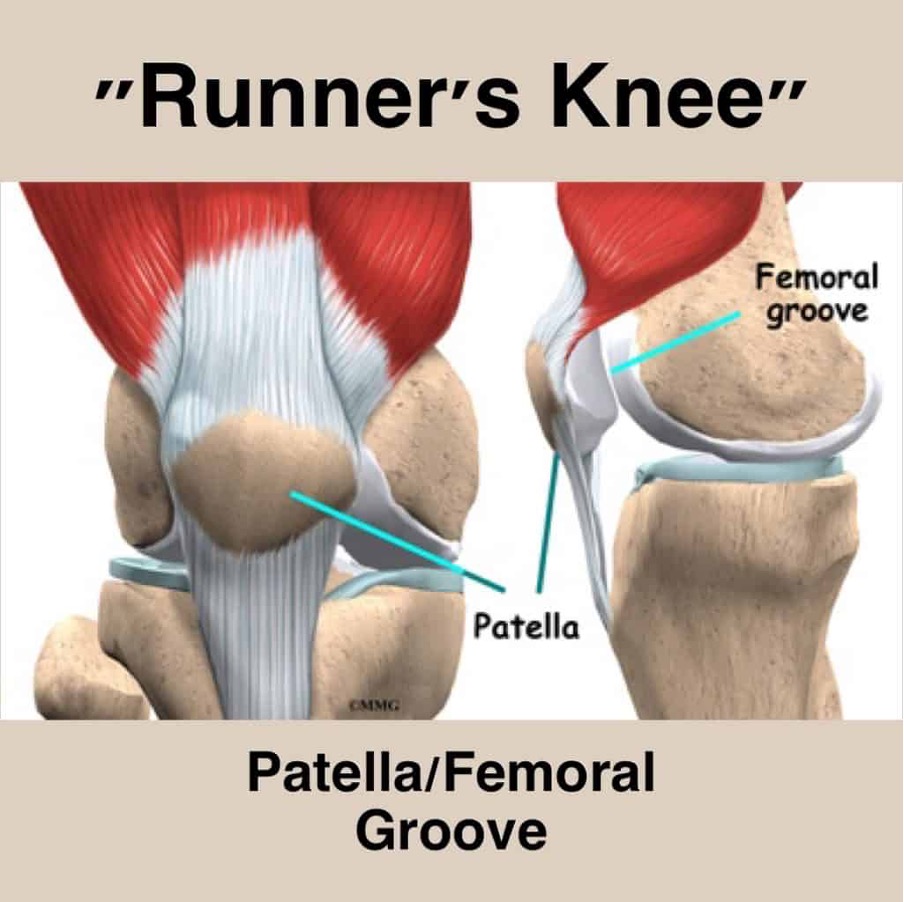
Understanding Runner’s Knee is the first step to effectively managing the condition. Runner’s Knee is a term used to describe a variety of knee pain that is common in runners, but can also affect other athletes and active individuals. The pain is typically felt around or behind the kneecap and can be caused by a number of factors, including overuse or improper form. It is important to pinpoint the cause of the pain in order to develop an effective treatment plan. By understanding the underlying causes and symptoms of Runner’s Knee, individuals can take steps to prevent and manage the condition, allowing them to continue enjoying their favorite activities pain-free.
Causes of Runner’s Knee
After understanding what runner’s knee is, the next step is to identify the causes behind it. Generally, runner’s knee is caused by issues with the alignment of the kneecap, leading to friction and discomfort in the area. This misalignment can be the result of weak muscles in the legs and hips, overuse of the knee joint, or injury to the soft tissue surrounding the kneecap.
It’s essential to diagnose the underlying cause correctly to identify the correct treatment plan. Simple treatments such as rest, ice, and stretching can alleviate symptoms and aid healing. However, a severe case may require medical intervention such as physical therapy or surgery. Understanding the causes of runner’s knee can help you identify ways to prevent it from happening in the first place.
Symptoms of Runner’s Knee
Runner’s knee is a common problem for anyone who loves running or other high-impact sports. It can bring a dull, aching pain to the knee, along with swelling, and popping sounds. The symptoms are due to the irritation of the soft tissues around the kneecap caused by repeated or prolonged bending of the knee. Besides the pain, people with runner’s knee may feel a grinding or rubbing sensation in their knee while walking, running, or climbing stairs. The symptoms can vary from person to person, but the discomfort is inevitable if left untreated.
The good news is, there are various treatment options that can help manage the symptoms and prevent runner’s knee from getting worse. However, one must be aware of the causes and risk factors that lead to runner’s knee to address it better. Therefore, it is essential to understand the various aspects of runner’s knee, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and exercises to help build strong knees.
Diagnosis of Runner’s Knee
To properly address and treat Runner’s Knee, it’s important to get a proper diagnosis. Your healthcare provider can diagnose Runner’s Knee by looking at your health history and doing a physical exam. X-rays may be needed for further evaluation of the knee. This condition is also known as patellofemoral pain syndrome and is more common in people who run and participate in sports that involve running. A physical exam tests the stability, motion and function of the knee, and the physician will evaluate the knee for symptoms such as swelling and stiffness.
In addition to sports and exercise, symptoms of patellofemoral pain syndrome will be present with bending of the knee again and again or overuse. When the knee cap is tender to the touch, it’s an acute case of Runner’s Knee. A complete diagnosis ensures a tailored treatment plan, which may include exercises or physical therapy, and proper stretching before a run to prevent further complications. If symptoms persist, it is important to seek medical attention.


